On February 28, 2022, the latest Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) report was released. Not surprisingly, it showed how human-induced climate change is causing dangerous and widespread disruption in nature and affecting the lives of billions of people around the world, despite efforts to reduce the risks. People and ecosystems least able to cope are being hardest hit.
But it also made a “new” point that—while familiar to those of us in the business of restoring the planet and our climate—needs to be better-known among policymakers: the problem of maladaptation, which was discussed in the 2020 book, RECONOMICS: The Path To Resilient Prosperity.
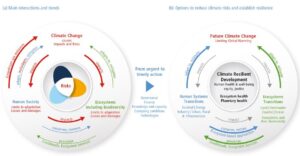 Maladaptation comprises efforts to boost local resilience that actually make the global problem worse.
Maladaptation comprises efforts to boost local resilience that actually make the global problem worse.
Such approaches are often adopted when powerful AEC firms influence local politicians to fund costly, palliative civil engineering projects. This is made worse when governments use antiquated “cost-plus” contracts, which pretty much guarantee the most expensive approach.
They also occur when large, old civil engineering institutions (such as the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers) take a “business as usual” approach…simply doing the simplistic wall-building projects they’ve done for two centuries, with little attention paid to more advanced, integrated solutions.
“Hard engineering structures, such as seawalls, have historically been the primary approach to coastal hazard reduction,” says Melanie Bishop, an associate professor of marine ecology at Macquarie University in Sydney, NSW, Australia.
“While these structures have in many instances effectively protected coastal assets from erosion and inundation, their use has come at considerable cost – not only in economic terms, but also environmentally and socially,” she explained.
The world faces unavoidable multiple climate hazards over the next two decades with global warming of 1.5°C (2.7°F).
Even temporarily exceeding this warming level will result in additional severe impacts, some of which will be irreversible. Risks for society will increase, including to infrastructure and low-lying coastal settlements.
“Healthy ecosystems are more resilient to climate change and provide life-critical services such as food and clean water,” said IPCC Working Group II Co-Chair Hans-Otto Pörtner.
“By restoring degraded ecosystems and effectively and equitably conserving 30 to 50 per cent of Earth’s land, freshwater and ocean habitats, society can benefit from nature’s capacity to absorb and store carbon, and we can accelerate progress towards sustainable development, but adequate finance and political support are essential,” he continued.
Urgent action required to deal with increasing risks
Increased heatwaves, droughts and floods are already exceeding plants’ and animals’ tolerance thresholds, driving mass mortalities in species such as trees and corals.
These weather extremes are occurring simultaneously, causing cascading impacts that are increasingly difficult to manage. They have exposed millions of people to acute food and water insecurity, especially in Africa, Asia, Central and South America, on Small Islands and in the Arctic.
To avoid mounting loss of life, biodiversity and infrastructure, ambitious, accelerated action is required to adapt to climate change, at the same time as making rapid, deep cuts in greenhouse gas emissions.
So far, progress on adaptation is uneven and there are increasing gaps between action taken and what is needed to deal with the increasing risks, the new report finds. These gaps are largest among lower-income populations.
The Working Group II report is the second instalment of the IPCC’s Sixth Assessment Report (AR6), which will be completed this year.
“This report is a dire warning about the consequences of inaction,” said Hoesung Lee, Chair of the IPCC. “It shows that climate change is a grave and mounting threat to our wellbeing and a healthy planet. Our actions today will shape how people adapt and nature responds to increasing climate risks.”
“This report recognizes the interdependence of climate, biodiversity and people and integrates natural, social and economic sciences more strongly than earlier IPCC assessments,” added Lee. “It emphasizes the urgency of immediate and more ambitious action to address climate risks. Half measures are no longer an option.”
Safeguarding and strengthening nature is key to securing a livable future
There are options to adapt to a changing climate. This report provides new insights into nature’s potential not only to reduce climate risks but also to improve people’s lives.
Scientists point out that climate change interacts with global trends such as unsustainable use of natural resources, growing urbanization, social inequalities, losses and damages from extreme events and a pandemic, jeopardizing future development.
“Our assessment clearly shows that tackling all these different challenges involves everyone – governments, the private sector, civil society – working together to prioritize risk reduction, as well as equity and justice, in decision-making and investment,” said IPCC Working Group II Co-Chair Debra Roberts.
“In this way, different interests, values and world views can be reconciled. By bringing together scientific and technological know-how as well as Indigenous and local knowledge, solutions will be more effective. Failure to achieve climate resilient and sustainable development will result in a sub-optimal future for people and nature,” she added.
Cities: Hotspots of impacts and risks, but also a crucial part of the solution
This report provides a detailed assessment of climate change impacts, risks and adaptation in cities, where more than half the world’s population lives.
People’s health, lives and livelihoods, as well as property and critical infrastructure, including energy and transportation systems, are being increasingly adversely affected by hazards from heatwaves, storms, drought and flooding as well as slow-onset changes, including sea level rise.
“Together, growing urbanization and climate change create complex risks, especially for those cities that already experience poorly planned urban growth, high levels of poverty and unemployment, and a lack of basic services,” Roberts explained.
“But cities also provide opportunities for climate action – green buildings, reliable supplies of clean water and renewable energy, and sustainable transport systems that connect urban and rural areas can all lead to a more inclusive, fairer society,” she concluded.
There is increasing evidence of adaptation that has caused unintended consequences, for example destroying nature, putting peoples’ lives at risk or increasing greenhouse gas emissions. This can be avoided by involving everyone in planning, attention to equity and justice, and drawing on Indigenous and local knowledge.
A narrowing window for action
Climate change is a global challenge that requires local solutions and that’s why the Working Group II contribution to the IPCC’s Sixth Assessment Report (AR6) provides extensive regional information to enable Climate Resilient Development.
The report clearly states Climate Resilient Development is already challenging at current warming levels. It will become more limited if global warming exceeds 1.5°C (2.7°F). In some regions it will be impossible if global warming exceeds 2°C (3.6°F).
This key finding underlines the urgency for climate action, focusing on equity and justice. Adequate funding, technology transfer, political commitment and partnership lead to more effective climate change adaptation and emissions reductions.
“The scientific evidence is unequivocal: climate change is a threat to human wellbeing and the health of the planet. Any further delay in concerted global action will miss a brief and rapidly closing window to secure a liveable future,” concluded Pörtner.
The Summary for Policymakers of the IPCC Working Group II report, Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability was approved on February 27 2022, by 195 member governments of the IPCC.
Photo of sea wall courtesy of USACE.

